The Development of Health and the Progress of Human Rights in China (full text)
Xinhua News Agency, Beijing, September 29th-The Press Office of the State Council published a white paper entitled "The Development of Health and the Progress of Human Rights in China" on September 29th. The full text is as follows:
The Development of Health and the Progress of Human Rights in China
People’s Republic of China (PRC) the State Council press office
September 2017
catalogue
foreword
First, the right to health protection model in line with national conditions
Second, the healthy environment and conditions continued to improve.
Third, the capacity of public health services has been steadily improved
Fourth, the quality of medical and health services has been greatly improved.
Five, the national medical security system gradually improved.
Six, the health level of specific groups has improved significantly.
7. Actively participate in global health governance and international medical assistance.
Concluding remarks
foreword
Health is the basic condition for human survival and social development. The right to health is an inclusive basic human right and the basic guarantee for human beings to live with dignity. Everyone has the right to enjoy the highest fair and accessible health standard.
The governments of the Communist Party of China (CPC) and China always adhere to the people-centered development thought, pursue the value orientation of people first, firmly grasp the people’s yearning for a better life, and take promoting people’s well-being and all-round development as the starting point and end result of development. Over the years, China has persisted in serving the people’s health, taking improving people’s health level and realizing health for all as an important development goal. After a long and unremitting struggle, China has significantly improved the people’s health level, not only shed the stigma of "the sick man of East Asia", but also continuously improved the overall strength of public health, medical services and security capabilities, and continuously enhanced the physical fitness and health literacy of the whole people, and was praised by the World Health Organization as "a model of developing countries".
Without national health, there will be no overall well-off society. Realizing national health is a solemn commitment of the governments of the Communist Party of China (CPC) and China to the people. Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, under the strong leadership of the CPC Central Committee with the Supreme Leader as the core, China has put people’s health in a strategic position of giving priority to development, and put the development concept of innovation, coordination, green, openness and sharing into the promotion and protection of the right to health, focusing on popularizing healthy life, optimizing health services, improving health security, building a healthy environment and developing health industries, accelerating the construction of healthy China, and striving to provide people with health and health services throughout their life cycle.
First, the right to health protection model in line with national conditions
China is a large developing country with a population of more than 1.3 billion. The governments of the Communist Party of China (CPC) and China have always attached great importance to the development of health and health undertakings, accelerated the transformation of the development mode in the health field, earnestly respected and guaranteed citizens’ right to health, and formed a health right protection model in line with national conditions.
When New China was founded in 1949, the level of economic and social development was relatively backward, and the medical and health system was very weak. There were only 3,670 medical and health institutions in China, with 541,000 health workers and 85,000 beds, and the average life expectancy was only 35 years. In order to change this situation as soon as possible, the state has made great efforts to develop medical and health undertakings, formulated and implemented the working policy of "facing workers, peasants and soldiers, putting prevention first, uniting Chinese and Western medicine, and combining health work with mass movements", extensively carried out mass patriotic health campaigns, popularized primary health care, greatly improved people’s health, made a major breakthrough in medical technology, isolated Chlamydia trachomatis for the first time, performed the world’s first limb replantation operation, and successfully developed artemisinin, a new antimalarial drug.
After the reform and opening up in 1978, in view of the serious shortage of medical and health resources, insufficient service capacity and low service efficiency, the state implemented multi-channel financing, encouraged various forms of medical services, increased the supply of resources, gradually liberalized the pharmaceutical production and circulation market, developed the pharmaceutical industry, paid attention to the role of Chinese medicine, and adopted certain economic incentives to mobilize the enthusiasm of medical staff and enhance internal vitality. In 1996, the first national conference on health work defined the policy of health work in the new period, which is "focusing on rural areas, giving priority to prevention, paying equal attention to Chinese and Western medicine, relying on science and technology and education, mobilizing the whole society to participate, serving people’s health and socialist modernization". In 1998, the state began to establish a social medical insurance system to ensure the basic medical needs of employees. In 2000, the state put forward the reform goal of establishing a medical and health system in cities and towns to meet the requirements of the socialist market economy, so that people can enjoy medical services with reasonable prices and excellent quality and improve people’s health. In 2002, the state issued the "Decision on Further Strengthening Rural Health Work", proceeding from the reality of rural economic and social development, deepening the reform of rural health system and mechanism, tilting the focus of health investment to rural areas to meet the medical and health needs of farmers at different levels.
In 2003, under the strong leadership of the party and the government, the people of the whole country were United as one and achieved a major victory in the fight against SARS. On the basis of summing up experience, the state has comprehensively strengthened public health services and the prevention and control of major diseases, continuously improved the prevention and control system of major diseases, gradually improved the emergency mechanism for public health emergencies, accelerated the pace of medical and health development in rural and urban communities, and made breakthroughs in the new rural cooperative medical care and basic medical insurance for urban residents.
In 2009, the state launched a new round of medical and health system reform, and promulgated the Opinions on Deepening the Reform of Medical and Health System, which established the core concept of providing basic medical and health system to the whole people as a public product, further clarified the public welfare nature of public medical and health, and put forward the establishment of "four systems" of public health, medical services, medical security and drug supply, as well as medical and health management, operation, investment, price, supervision, science and technology, talents and information. Subsequently, the state promulgated the Key Implementation Plan for Medical and Health System Reform in the Near Future (2009-2011) and the Plan and Implementation Plan for Deepening the Reform of Medical and Health System during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, proposing reform tasks such as accelerating the construction of the basic medical security system, improving the primary medical and health service system, and promoting the gradual equalization of basic public health services.
Since 2012, China has continuously intensified the reform of the medical and health system, accelerated the comprehensive reform of public hospitals, promoted the price reform of drugs and medical services, fully implemented the serious illness insurance for urban and rural residents, actively built a graded diagnosis and treatment system, and optimized and improved the policy of drug production, circulation and use. On October 29th, 2015, Healthy China Construction was officially written into the communiqué of the Fifth Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee. In August 2016, the National Health and Wellness Conference put forward: "We must adhere to the correct health and wellness work policy, focus on the grassroots, take reform and innovation as the driving force, give priority to prevention, pay equal attention to both Chinese and Western medicine, integrate health into all policies, and build and share with the people." In October, 2016, the state promulgated the Outline of Healthy China 2030, which made strategic arrangements for promoting the construction of healthy China and improving people’s health.
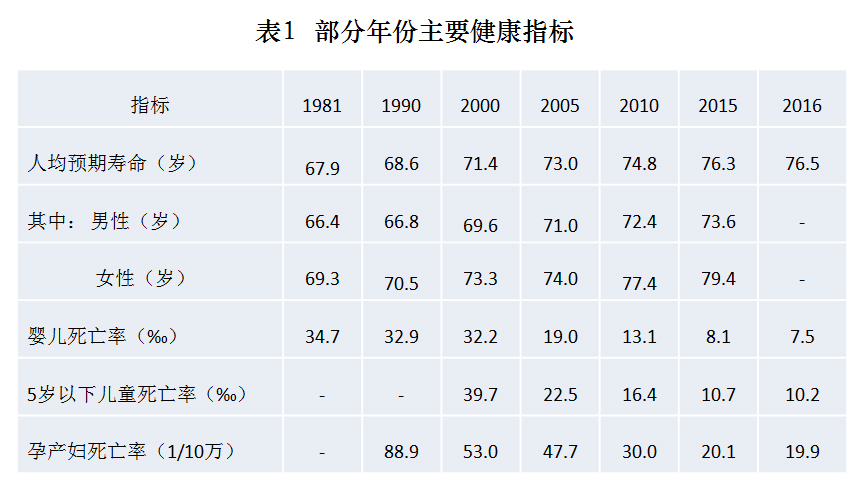
The development of health has brought tangible health benefits to the people. The average life expectancy in China has increased from 67.9 years in 1981 to 76.5 years in 2016, the maternal mortality rate has decreased from 88.9 per 100,000 in 1990 to 19.9 per 100,000 in 2016, and the infant mortality rate has increased from 34.7&permil 100,000 in 1981. Down to 7.5&permil in 2016; On the whole, the main health indicators of residents are better than the average level of middle-and high-income countries, achieving the UN Millennium Development Goals ahead of schedule. At the same time, China has formed a health system based on the Constitution, civil laws and regulations, health administrative laws and regulations, local regulations, etc., and guided by various outlines, programs and plans in the health field, effectively balancing the relationship between doctors and patients, fairly resolving medical disputes, and effectively realizing citizens’ right to health.
The effect of deepening medical reform has been continuously highlighted. In a short period of time, the world’s largest national basic medical security network has been woven, a serious illness insurance system, a disease emergency rescue system and a sound medical assistance system have been established, providing institutional guarantee for realizing medical care for the sick. Major infectious diseases have been effectively controlled, the overall epidemic situation of AIDS has been controlled at a low epidemic level, the tuberculosis control targets set by the United Nations Millennium Development Goals have been achieved ahead of schedule, the epidemic situation of schistosomiasis has dropped to the lowest level in history, and the goal of polio-free in 2000 has been achieved. In 2015, the world’s largest online direct reporting system for legal infectious diseases and public health emergencies was established, and the average reporting time was shortened from five days before direct reporting to four hours.
Significant progress has been made in the construction of the medical and health service system, and a basic medical and health service network covering urban and rural areas has been basically established. There are more than 980,000 medical and health institutions at all levels, with more than 11 million health workers and more than 7 million beds in health institutions. The construction of talent team has been accelerated, the standardized training system for residents has been gradually established, and a number of outstanding medical workers such as Tu Youyou, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, have emerged. The development of social medical services has accelerated, and the proportion of private hospitals in the total number of hospitals has exceeded 57%, and the pattern of diversified medical services has initially taken shape. The medical and health emergency rescue capability is in the forefront of the world, and it has withstood the severe test of preventing and controlling the epidemic situation of Ebola hemorrhagic fever, and achieved the double victory of "strict prevention and control, zero input" and "winning the battle and zero infection" in aiding Africa to fight the epidemic.
After long-term efforts, the development of health and health undertakings in China has reached a new level, which not only significantly improved the people’s health level, but also formed a health right protection model in line with China’s national conditions. Its main features are:
— — Give priority to health, put health in a strategic position of giving priority to development, integrate the concept of maintaining and promoting health into the whole process of formulating and implementing policies, laws and regulations based on national conditions, and realize healthy lifestyle, production conditions and benign and coordinated development of ecological environment and economy and society.
— — Give priority to prevention, change the focus on treatment to focus on people’s health, adhere to the combination of prevention and treatment, pay equal attention to both body and mind, complement Chinese and western medicine, pay attention to the prevention and control of chronic diseases, endemic diseases and occupational diseases, reduce the occurrence of diseases, grasp the development law in the health field, and strengthen early diagnosis, early treatment and early rehabilitation.
— — Public welfare-oriented, adhere to the public welfare of basic medical and health undertakings, provide the basic medical and health system as a public product to the whole people, and take public hospitals as the main body of the medical service system, so as to gradually realize the universal access to public health services.
— — Fair and inclusive, adhere to the coverage of health services and medical security for the whole people, focus on rural areas and grassroots units, gradually narrow the differences in health levels between urban and rural areas, regions and different groups of people, and ensure the equalization of basic public services in the health field.
— — Co-construction and sharing, adhering to the combination of government leadership and mobilizing the enthusiasm of society and individuals, promoting everyone’s participation, everyone’s efforts and everyone’s enjoyment, correctly handling the relationship between the government and the market, the government has made a difference in the field of basic medical and health services, and the market has exerted its vitality in the field of non-basic medical and health services.
Second, the healthy environment and conditions continued to improve.
China actively promotes a healthy lifestyle, launches a nationwide fitness campaign, promotes nationwide health education, ensures the safety of food and drinking water, and improves the production, living, ecological and social environment, thus providing good conditions for promoting citizens’ right to health.
Healthy lifestyle is fully implemented. In 2007, the state launched the national healthy lifestyle campaign, advocating residents to eat reasonably and exercise moderately, spreading the concept of healthy lifestyle, creating a healthy supporting environment, and improving the health awareness and healthy behavior ability of the whole people. By the end of 2016, 81.87% of counties (districts) across the country had carried out this action. The "Dietary Guidelines for China Residents (2016)" was issued to provide scientific and reasonable dietary guidance to the general population and specific groups such as children and the elderly, so as to guide residents to achieve a balanced diet and balanced nutrition. Promote the monitoring of nutrition and health status of residents, as well as the monitoring and release of chronic diseases and nutrition. Carry out the national salt reduction initiative to teach residents health knowledge such as salt reduction, prevention and control of hypertension. Implement nutrition improvement measures for key populations, carry out nutrition improvement plans for rural compulsory education students and nutrition improvement projects for children in poverty-stricken areas. Continue to strengthen tobacco control and fulfill the provisions of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. In 2014, Shenzhen implemented the Regulations on the Control of Smoking in Shenzhen Special Economic Zone, in 2015, Beijing implemented the Regulations on the Control of Smoking, and in 2017, Shanghai implemented the amendment to the Regulations on the Control of Smoking in Public Places in Shanghai, so as to implement the requirement of comprehensive indoor smoking ban. By the end of 2016, 18 cities across the country had formulated local smoke-free environmental laws and regulations, covering one tenth of the total population.
The national fitness campaign is flourishing. Promote the cause of national fitness to a national strategy, and incorporate the work of national fitness into the national economic and social development plans, financial budgets and annual work reports of governments at all levels. The development pattern of "government-led, departmental cooperation and the participation of the whole society" has initially taken shape. Since the promulgation of the National Fitness Regulations in 2009, 16 provinces and 10 large cities have formulated local laws and regulations on national fitness, and all 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) have completed the provincial National Fitness Implementation Plan. Since 2009, the state has designated August 8th as "National Fitness Day". From 2011 to 2014, 3,405 national fitness activity centers, 9,447 community multi-functional sports grounds, 2,366 sports parks, 24,879 fitness plazas, 878 outdoor camps and 1.69 million outdoor fitness equipment have been built nationwide. All cities (prefectures), counties (districts), streets (townships, towns) and communities (administrative villages) have generally built sports venues with fitness facilities. By the end of 2015, the proportion of people who regularly participate in physical exercise in China has reached 33.9%, the per capita sports area has reached 1.57 square meters, the average coverage rate of sports associations at county level and above has reached 72%, there are 7,147 youth sports clubs at all levels, and the average number of national fitness stations has reached 3 per 10,000 people. The socialized national fitness organization network has basically taken shape.
Health education for all continued to advance. Make full use of newspapers, television, radio, internet and new media to carry out public health publicity and education consultation, and guide residents to form a healthy lifestyle of self-discipline. The state holds "China Environment and Health Publicity Week" every year. China citizens’ environmental and health literacy (for Trial Implementation) and "code of conduct for citizens who share the same breath and struggle together" were issued. Carry out health publicity and education through basic public health service health education, health literacy promotion action, health trip to China, Chinese medicine trip to China, major health theme publicity day and other projects and activities. The level of health literacy of urban and rural residents rose from 6.48% in 2008 to 10.25% in 2015.
Environmental governance has been deepened. Strengthen regional joint prevention and control, realize the networking of county-level air quality monitoring stations in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta, and complete the particulate matter composition and photochemical monitoring network in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding areas. From 2011 to 2015, the national chemical oxygen demand and the total discharge of ammonia nitrogen, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides decreased by 12.9%, 13%, 18% and 18.6% respectively. In 2016, the average concentration of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in 338 cities at prefecture level and above decreased by 6.0% year-on-year, and the number of excellent days increased by 2.1 percentage points year-on-year. In 2013, the state promulgated and implemented the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. From 2014 to 2016, more than 16 million yellow-label vehicles and old vehicles were eliminated. Coal-fired thermal power units basically achieve full coverage of desulfurization and denitrification. The ultra-low emission has been accelerated. As of March 2017, the ultra-low emission transformation of coal-fired power units has been completed by about 500 million kilowatts. Implement the Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Soil Pollution, and start a detailed investigation of soil pollution in an all-round way. Promulgated the Measures for the Management of Soil Environment in Polluted Plots (for Trial Implementation) and set up special funds for the prevention and control of soil pollution. In 2016 and 2017, the state allocated a total of about 15 billion yuan of special funds. The national soil environment network was initially established, 22,000 basic points were laid out, and about 15,000 risk monitoring points were built. Comprehensively promote the implementation of the Action Plan for Water Pollution Prevention and Control. Strengthen the comprehensive management of river basin water environment. Implement the great protection work of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and organize the investigation of urban black and odorous water bodies. In 2016,The proportion of I-III water bodies in the national surface water monitoring section reached 67.8%, and the proportion of inferior V water bodies decreased to 8.6%.
The comprehensive improvement of urban and rural environmental sanitation has achieved remarkable results. Carry out activities to create sanitary towns and significantly improve the quality of urban and rural human settlements. According to the survey in 2012, compared with before the establishment of sanitary towns, the proportion of standardized markets has increased from 35.2% to 60.6%, the satisfaction rate of residents with the city appearance and environment has increased from 30% to 98%, and the satisfaction rate with the health creation effect has reached 98%. By the end of 2015, the national urban sewage treatment rate has increased to 92%, and the harmless treatment rate of domestic garbage in urban built-up areas has reached 94.1%. Comprehensive environmental improvement was carried out in 78,000 villages, directly benefiting more than 140 million rural people. 61,000 large-scale farms (communities) have built waste treatment and resource utilization facilities. By the end of 2016, the national rural domestic waste treatment rate was around 60%, and the proportion of administrative villages that treated sewage reached 22%. The penetration rate of sanitary toilets in rural areas increased from 71.7% in 2012 to 80.4% in 2016, and reached more than 90% in some eastern provinces.
The problem of drinking water safety in rural areas has been basically solved. From 2006 to 2010, the total investment of rural drinking water safety project construction was 105.3 billion yuan, which solved the drinking water safety problem of 190,000 administrative villages and 212 million rural population. From 2011 to 2015, the state allocated a total of 121.5 billion yuan for rural drinking water safety construction projects and more than 60 billion yuan for local matching funds. By the end of 2016, the coverage rate of rural drinking water safety and sanitation monitoring reached over 85%, and the proportion of rural centralized water supply coverage increased to 82%. In view of the special difficulties in individual areas, the state has arranged special funds to raise the subsidy standard, and arranged 495 million yuan to solve the drinking water safety problem of more than 1,400 temples, 32,300 monks and nuns and more than 60,000 people with temporary water supply in Xizang Autonomous Region.
Occupational health management has been continuously strengthened. In 2011, the state revised the Law on the Prevention and Control of Occupational Diseases in People’s Republic of China (PRC), vigorously carried out special treatment of dust and toxic hazards in key areas, and organized centralized rectification of industries with serious dust hazards, such as quartz sand processing, asbestos mining and product manufacturing, gold mining, cement manufacturing, stone processing, ceramic production and refractory manufacturing, and urged enterprises to increase investment, improve production technology, improve protective facilities and strengthen individual protection. The working environment and conditions in the workplace have been initially improved. By the end of 2016, the state had punished a number of enterprises that refused to govern or had poor governance according to law, ordered 1,524 enterprises to stop production and rectify, requested 1,576 enterprises to close down and banned 426 illegal enterprises. Strengthen the supervision and inspection of occupational health of employers. From 2013 to 2016, the number of supervision and inspection enterprises in various regions of the country increased from 229,000 to 395,000, an increase of 72.5%.
Food safety supervision is stricter. In 2015, the State revised the Food Safety Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC). In 2016, regulatory agencies at all levels inspected food production enterprises for 521,000 times and food additive production enterprises for 15,000 times. Inspected 72,000 small food processing workshops. Regulators at all levels have inspected 12.093 million business entities in the food business. 8.869 million business entities in catering services were inspected. In 2016, 257,000 batches of food samples were sampled nationwide, with an overall pass rate of 96.8%. Properly handle many food safety emergencies such as counterfeit infant formula milk powder.
Third, the capacity of public health services has been steadily improved
China insists on putting prevention first, combining prevention with treatment, improving the accessibility and equality of public health services, intensifying the prevention and control of infectious diseases, chronic diseases, endemic diseases and other diseases, enhancing the emergency response capability of public health emergencies, and implementing basic public health services covering the whole people, with the degree of equality constantly improving.
The coverage rate of basic public health services has been further improved. The state provides vaccines and vaccination services free of charge, and the beneficiaries have expanded from children to adults. By the end of 2015, the vaccination rate remained above 90% in villages and towns as a whole, and most immunization programs could prevent the incidence and mortality of infectious diseases from falling to the lowest level in history. From 2010 to 2017, the per capita financial subsidy standard for basic public health services was raised from 15 yuan to 50 yuan, and the service items were expanded from the initial 41 items in 9 categories to 47 items in 12 categories. Twelve types of services have been established, including residents’ health records, health education, vaccination, children’s health management, maternal health management, elderly health management, chronic patients’ health management, patients with severe mental disorders’ health management, tuberculosis patients’ health management, Chinese medicine health management, reporting and handling of infectious diseases and public health emergencies, and health and family planning supervision and assistance, which have basically covered the whole life process of residents. By the end of 2016, the filing rate of electronic health records of residents in China reached 76.9%, and the number of health managers of patients with hypertension and diabetes reached 90.23 million and 27.81 million respectively. The systematic management rate of pregnant women and children under 3 years old reached 91.6% and 91.1% respectively.
The coverage of basic public health services is constantly expanding. In 2012, the country achieved the goal of eliminating neonatal tetanus. In 2014, through the vaccination of newborns with hepatitis B vaccine, the HBsAg carrying rate of children under 5 years old decreased from 9.67% in 1992 to 0.32%, thus achieving the goal of reducing the HBsAg prevalence rate of people under 5 years old to below 1% in 2017 ahead of schedule proposed by the World Health Organization. The utilization of basic public health services of floating population has been continuously improved, and the prevention and control of infectious diseases has been widely carried out. The immunization rate of floating children has reached over 90%. In view of major diseases, important health risk factors and health problems of key populations, major public health service projects have been formulated and implemented, covering nearly 200 million people in total, such as replanting hepatitis B vaccine for people under 15, improving nutrition for children in poor areas, providing hospital delivery for pregnant women in rural areas, screening for "two cancers" for rural women, and building harmless sanitary toilets in rural areas. In 2009, the state launched the "Vision Restoration Project for Millions of Poor Cataract Patients", and the government provided subsidies for poor cataract patients to perform vision restoration surgery. By the end of 2013, the number of people undergoing surgery had exceeded 1.75 million.
The level of epidemic control of infectious diseases has been continuously improved. The country has built the world’s largest online direct reporting system for legal infectious diseases and public health emergencies. The reported incidence of legal infectious diseases decreased by 19.4% on average. The ability of early detection and early warning of infectious diseases has been further enhanced. The infectious disease information reporting system covers nearly 71,000 medical institutions, with more than 160,000 users, and reports about 9 million pieces of case information every year. In 2016, the reported incidence and mortality of Class A and B infectious diseases in China were controlled below 215.7/100,000 and 131/100,000 respectively. A national, provincial, municipal and county-level laboratory testing network has been established, and laboratories such as influenza, polio, measles and Japanese encephalitis of China CDC have become reference laboratories of the World Health Organization. The epidemic situation is generally stable, and no major infectious diseases have occurred. The overall epidemic situation of AIDS has been controlled at a low epidemic level, and the rapid rise of the epidemic situation in key areas has been basically curbed. The prevention and treatment of tuberculosis has achieved remarkable results, and the successful treatment rate has remained above 90%. In 2016, the number of reported cases of tuberculosis in China decreased by 12.6% compared with 2011, and the mortality rate of tuberculosis dropped to about 2.3/100,000, reaching the level of developed countries; A total of 3,189 cases of malaria were reported in China, of which only 3 cases were infected locally, which was significantly lower than 4,262 cases in 2010. More than 80% of malaria-endemic counties basically eliminated malaria. The prevention and control effect of key parasitic diseases has been continuously consolidated. By the end of 2016, all 453 endemic counties in China had reached the standard of schistosomiasis transmission control or above.
The effect of prevention and control of chronic diseases has been significantly enhanced. The state has established a monitoring network for chronic diseases and risk factors of chronic diseases. Health management of the elderly and management of patients with hypertension and diabetes are provided to the public free of charge as national basic public health services, and projects such as high-risk screening of stroke and cardiovascular diseases, comprehensive intervention of oral diseases, and early diagnosis and treatment of cancer are implemented. By the end of 2016, more than 6.1 million people had been screened by the screening and intervention project for high-risk groups of stroke, 820,000 high-risk groups were found and 952,000 follow-up interventions were carried out; A total of 3.389 million people were screened in the early screening and comprehensive intervention project for high-risk groups of cardiovascular diseases, and 776,000 people were found in high-risk groups, and 524,000 people were followed up. The comprehensive intervention project for children’s oral diseases provides 100 million children with free oral examination, 5.168 million children with free pit and fissure sealing, and 2.229 million children with free local fluoride; The cancer early diagnosis and treatment project has screened 2.14 million high-risk groups and found 55,000 patients, with an overall early diagnosis rate higher than 80%.
The epidemic trend of endemic diseases has been effectively controlled. By the end of 2015, the consumption rate of non-iodized salt in 90.8% counties in water-source high-iodine areas in China was above 90%, and 94.2% counties remained in the state of eliminating iodine deficiency disorders, which was at the leading level among 128 countries and regions in the world that adopted salt iodization measures. 95.4% of villages in Kaschin-Beck disease areas reached the elimination standard, and 94.2% of counties in Keshan disease areas reached the control standard. The rate of changing stoves to stoves in all counties in coal-burning endemic fluorosis areas reached 98.4%, and 93.6% of rural population in drinking water endemic fluorosis areas implemented the project of reducing fluoride and improving water. All the areas with endemic arsenism caused by coal burning pollution have been changed into stoves, and all the areas with endemic arsenism caused by drinking water have been changed into water.
Mental health services have been continuously improved. The State promulgated and implemented the Mental Health Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC), bringing mental health work into the track of rule of law. By the end of 2015, there were 2,936 mental health service institutions in China, with 433,000 beds, up 77.9% and 89.9% respectively over 2010. There are 27,700 practicing (assistant) psychiatrists, an increase of 20.2% compared with 23,100 at the end of 2012. Serious mental disorders were included in the coverage of major diseases covered by the new rural cooperative medical system and urban residents’ medical insurance, and the central government subsidized local management and treatment projects for serious mental disorders. In some areas, special policies for treatment and assistance were introduced, reducing the burden on patients. Strengthen the registration of patients with severe mental disorders and the management of treatment and assistance. From 2012 to 2016, the number of registered patients with severe mental disorders in China increased from 3.08 million to 5.4 million, and the patient management rate increased from 59.1% to 88.7%. Strengthen the intervention of common mental disorders and psychological and behavioral problems such as depression and anxiety, increase the early detection and timely intervention of psychological problems of key groups, improve the intervention ability and level of unexpected psychological crisis, and comprehensively promote community rehabilitation services for mental disorders.
The ability to respond to public health emergencies has been comprehensively strengthened. The emergency legal system has been basically established, and the emergency mechanism has been continuously optimized. There are 36 national and nearly 20,000 local health emergency response teams with more than 200,000 people in four categories in different regions of the country. In 2014, the national public health emergency core competence compliance rate rose to 91.5%, far exceeding the global average of 70%. In recent years, the country has accelerated the construction of the health emergency system, effectively responding to the sudden acute infectious diseases such as human infection with H7N9 avian influenza, Ebola hemorrhagic fever, Middle East respiratory syndrome and Zika virus, as well as the emergency medical rescue and post-disaster health and epidemic prevention of a series of major disasters such as the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan and the fire and explosion accident in Tianjin Port.
Fourth, the quality of medical and health services has been greatly improved.
China is committed to improving the accessibility and convenience of medical and health resources, simultaneously promoting the continuous improvement of the quality and efficiency of medical services, accelerating the establishment of a high-quality and efficient integrated medical and health service system, continuously improving the drug supply system, and significantly improving the residents’ medical experience.
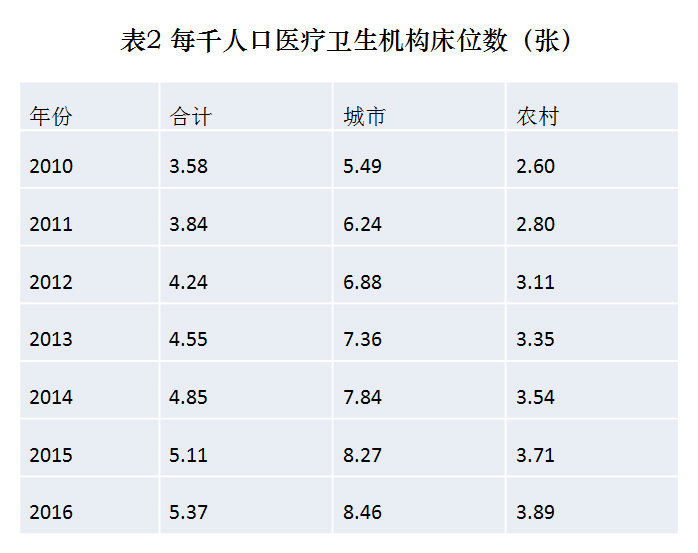
The resource elements of the medical and health service system continue to increase. From 2011 to 2015, the state invested 42 billion yuan, focusing on supporting the construction of more than 1,500 county-level hospitals, 18,000 township hospitals, more than 100,000 village clinics and community health service centers. By the end of 2016, there were 983,394 medical and health institutions in China, including 29,140 hospitals (12,708 public hospitals and 16,432 private hospitals), 36,795 township hospitals, 34,327 community health service centers (stations), 3,481 disease prevention and control centers, 2,986 health supervision stations (centers) and 63,300 village clinics. According to the national statistics, there are 5.291 million medical devices with a price of over 10,000 yuan, including 125,000 devices with a price of over 1 million yuan. In 2016, the number of beds in medical institutions increased by 395,000 compared with 2015, the number of beds per 1,000 population reached 5.37, and the number of beds in hospitals increased by 358,000; There are 266 ethnic minority medical hospitals in China, with 26,484 beds, with a total of 9.687 million visits and 588,000 discharges.
The medical and health personnel team is more optimized. China has built the largest medical education system in the world. By the end of 2016, there were 922 medical colleges and 1564 secondary schools offering medical education, with 238 master’s degree awarding units and 92 doctor’s degree awarding units, with a total of 3.95 million students, including 1.14 million students majoring in clinical medicine and 1.8 million students majoring in nursing. A total of 14 educational institutions across the country have set up minority medicine majors and traditional Chinese medicine majors, with about 170 thousand students. Colleges of traditional Chinese medicine in Yunnan, Guangxi, Guizhou and other places have successively set up professional directions such as Dai medicine, Zhuang medicine and Miao medicine. Some minority medical colleges and universities cooperate with Chinese medicine colleges and universities to jointly cultivate minority medical talents. By the end of 2016, there were 11.173 million health workers, 8.454 million health technicians, 2.31 doctors per 1,000 population, 81.2% practicing (assistant) doctors with college degree or above, and high-level professionals increased year by year. The number of nurses per thousand population reached 2.54, and the ratio of doctors to nurses reached 1:1.1.
Social forces have been increasing in running hospitals. Give priority to supporting social forces to set up non-profit medical institutions and promote the equal treatment of non-profit private hospitals and public hospitals. Encourage doctors to use their spare time, retired doctors to practice in primary health care institutions or open studios. The proportion of private hospitals in China exceeds 57%, the total number of beds in social medical and health institutions has increased by 81% compared with 2011, and the number of outpatients has accounted for 22% of the total number of outpatients in China. Up to now, more than 70% of the doctors who have registered for multi-point practice in the country have gone to social medical institutions to practice.
Medical conditions at the grassroots level and in rural areas have been further improved. From the medical and health system, medical service institutions, medical service personnel and other aspects to the grassroots and rural areas. County-level hospitals will be positioned as the medical and health centers in the county and the core of the rural three-level medical and health service network, and one or two county-level hospitals (including Chinese medicine hospitals) will be run well in each county (city). Basically, one health center will be built in each township, and one village clinic will be set up in each administrative village on average, with one village doctor for every thousand rural residents.
The supply of medical and health services is more hierarchical. Establish a "trinity" major disease prevention and control mechanism of professional public health institutions, comprehensive and specialized hospitals and primary medical and health institutions, strengthen the information sharing and interconnection mechanism, promote the integrated development of chronic disease prevention, treatment and management, and realize the combination of medical prevention and treatment. Establish a graded diagnosis and treatment system in an all-round way, guide the formation of a reasonable medical order of primary diagnosis, two-way referral, up-and-down linkage, rapid and slow division, and improve treatment — — Rehabilitation — — Service chain of long-term care. The appointment rate of tertiary hospitals nationwide reached 38.6%, and nearly 400 medical institutions set up day surgery centers. The contract service of family doctors has been carried out, and the residents’ satisfaction with the professional skills and service attitude of family doctors has reached more than 80%, and the people’s feelings of seeking medical treatment have been significantly improved.
The level of medical quality and safety has been continuously improved. Formulate the Medical Quality Management Measures, gradually establish and improve the medical quality management and control system, issue quality control indicators, and carry out information quality monitoring and feedback. Promote the management of clinical pathways in medical institutions, and formulate 1212 clinical pathways, basically covering common diseases and frequently-occurring diseases. Issue and implement the National Action Plan to Contain Bacterial Drug Resistance (2016-2020) to comprehensively control the problem of bacterial drug resistance. Strengthen the supervision of prescription and medication. In 2016, the utilization rate of antibacterial drugs among inpatients in China was 37.5%, which was 21.9 percentage points lower than that in 2011. The utilization rate of antibiotics in outpatient prescriptions was 8.7%, which was 8.5 percentage points lower than that in 2011. Medical liability insurance covers more than 90% of hospitals above the second level. We attach great importance to blood safety and blood supply. By the end of 2015, we have achieved full coverage of nucleic acid testing in blood stations, and the level of blood safety is basically the same as that in developed countries. Promote voluntary blood donation and rational clinical use of blood. In 2016, a total of 14 million people participated in unpaid blood donation, an increase of 6.1% over 2015, which basically met the demand for clinical blood. Organ donation has become the main source of organ transplantation after the death of citizens.
The drug supply guarantee system was further improved. The drug supply guarantee system based on the national essential drug system has made great progress. Compared with before the implementation of the system, the sales price of essential drugs has dropped by about 30% on average, and the zero-difference sales rate has been implemented in primary medical and health institutions, greatly reducing the burden of patients’ medication. The first round of national drug price negotiation pilot was launched. The purchase price of drugs such as hepatitis B and non-small cell lung cancer dropped by more than 50%, and the price was at a low level in the world. By the end of 2016, patients had reduced their expenses by nearly 100 million yuan. Improve the policy of ensuring the supply of rare diseases drugs. Increase the free supply of special drugs such as AIDS prevention and treatment. We will further promote medical innovation and implement major scientific and technological projects of "major new drug creation". From 2011 to 2015, a total of 323 innovative drugs were approved for clinical research, 16 innovative drugs such as ectinib were approved for production, 139 new chemical generic drugs were listed, more than 600 varieties of raw materials and more than 60 pharmaceutical companies reached the international advanced GMP requirements, and a number of large-scale medical equipment such as PET-CT and 128-row CT and high-end implantable interventional products such as brain pacemakers, interventional artificial heart valves and cochlear implants were approved for listing. We will promote the construction of a modern pharmaceutical distribution network throughout urban and rural areas, and the ability to ensure the supply of drugs in grassroots and remote areas will continue to improve.
The development of traditional medicine is more supported by the state. From 2013 to 2015, the state invested a special fund of 4.6 billion yuan to support the capacity building of Chinese medicine services. In 2016, the State issued the Outline of Strategic Planning for the Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2016-2030). The main business income of enterprises above designated size in Chinese medicine industry is 865.3 billion yuan, accounting for about one third of the main business income of enterprises above designated size in the national pharmaceutical industry. Since 2011, 49 scientific research achievements of traditional Chinese medicine have won national science and technology awards. Artemisinin and the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia and other Chinese and western medicine research results have attracted global attention.
Five, the national medical security system gradually improved.
China has vigorously promoted the construction of the medical security system, forming a multi-level, wide-ranging and universal medical security system with basic medical security as the main body and other forms of supplementary insurance and commercial health insurance as supplements, and initially realized that everyone enjoys basic medical security.
Basic medical insurance has achieved full coverage. Universal medical insurance with basic medical insurance for employees, basic medical insurance for urban residents and new rural cooperative medical care as the main body has been initially realized. By the end of 2016, the number of people participating in basic medical insurance in China exceeded 1.3 billion, and the coverage rate was stable at over 95%. In 2016, the state officially launched the integration of the basic medical insurance for urban residents and the new rural cooperative medical system, unified coverage, unified financing policy, unified security benefits, unified medical insurance catalogue, unified fixed-point management and unified fund management, and gradually established a unified basic medical insurance system for urban and rural residents nationwide, so as to realize the fair enjoyment of basic medical insurance rights and interests by urban and rural residents.
The ability and sustainability of basic medical insurance have been further enhanced. In 2016, the annual income and expenditure of the basic medical insurance fund for employees were 1,027.4 billion yuan and 828.7 billion yuan respectively, an increase of 421.2 billion yuan and 341.9 billion yuan respectively over 2012, with an average annual growth rate of 15.7% and 15.6% respectively; The annual income and expenditure of the basic medical insurance fund for urban residents were 281.1 billion yuan and 248 billion yuan respectively, which were 193.4 billion yuan and 180.5 billion yuan higher than that in 2012. In 2017, the financial subsidy standard for urban and rural residents’ basic medical insurance will continue to increase, and the per capita subsidy standard for all levels of finance will reach 450 yuan per person per year.
The level of basic medical insurance benefits has been gradually improved. In 2016, the maximum payment limit of the basic medical insurance for employees and the basic medical insurance fund for urban residents reached 6 times of the annual average salary of local employees and the annual per capita disposable income of local residents, respectively, and the proportion of hospitalization expenses within the policy scope was about 80% and 70% respectively. In 2017, the reimbursement rate of outpatient and hospitalization expenses of the new rural cooperative medical system was stable at around 50% and 70% respectively. The National Catalogue of Medicines for Basic Medical Insurance, Work Injury Insurance and Maternity Insurance (2017 Edition) contains 2,535 medicines in western medicine and Chinese patent medicine, which is 339 more than the old catalogue, with an increase of about 15%, and basically covers the therapeutic medicines in the National Catalogue of Essential Medicines (2012 Edition). For some patented exclusive drugs with great clinical value and high price, the government organized medical insurance drug negotiations and granted access to 36 drugs, covering a variety of malignant tumors, some rare diseases and chronic diseases. Some new medical rehabilitation projects are included in the scope of basic medical insurance payment.
The reform of payment methods for basic medical insurance was promoted in an orderly manner. More than 70% of the country actively explores payment methods such as payment by disease, payment by head, and payment by DRGs. Accelerate the nationwide networking of basic medical insurance and direct settlement of medical treatment in different places, and continue to promote the "one card" for medical treatment. By the end of August 2017, the whole country had basically realized the direct settlement of medical expenses in the insured area and the direct settlement of hospitalization expenses in different places in the province. Successfully carried out cross-provincial off-site medical expenses direct settlement network access. All provinces (including Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps) and all co-ordination areas in China have all been connected to the national basic medical insurance off-site medical settlement system. By the end of August 2017, 6,616 designated medical institutions for direct settlement of off-site medical expenses were opened.
The mechanism for ensuring serious illness for urban and rural residents has been continuously improved. We will fully implement serious illness insurance for urban and rural residents, take solving large medical expenses as the starting point, and constantly improve and improve the medical security system for serious and serious diseases. By the end of 2015, serious illness insurance for urban and rural residents had covered all urban and rural residents’ basic medical insurance participants. In 2016, serious illness insurance covered more than 1 billion urban and rural residents, and the payment ratio stipulated in the provincial serious illness insurance policies reached more than 50%, and the actual reimbursement ratio of beneficiaries increased by 10-15 percentage points.
The medical assistance mechanism has achieved remarkable results. The policy framework of medical assistance has been basically established, medical assistance has been effectively linked with serious illness insurance for urban and rural residents, and the urban-rural unification of medical assistance standards and assistance levels has been gradually realized. The scope of medical assistance has gradually expanded from the past urban and rural minimum living allowances and poor people to the poor, low-income family members and seriously ill patients in poor families due to illness. Trade unions at all levels actively organize and carry out medical mutual assistance activities for employees, help employees suffering from major diseases, and reduce the economic burden of sick employees. In 2016, the state arranged a total of 15.5 billion yuan of medical assistance subsidy funds (excluding disease emergency assistance subsidy funds), of which 92% of the funds were invested in the central and western regions and poverty-stricken areas, and a total of 82.565 million people received medical assistance, and 55.604 million people in need were subsidized to participate in basic medical insurance. The proportion of the rescued objects who are hospitalized within the annual relief limit is generally above 70%. Medical assistance services are more convenient and accessible, and 93% of the areas have achieved "one-stop" settlement of medical assistance and medical insurance expenses. Since 2013, the state has established a disease emergency rescue system, and through the establishment of a disease emergency rescue fund, patients who need emergency treatment but whose identities are unknown or clear and unable to pay medical expenses are treated. As of June 2017, about 640,000 patients have been rescued.
The level of medical security for the rural poor has gradually improved. In 2016, the state began to implement the health poverty alleviation project. Full coverage of medical insurance and serious illness insurance for urban and rural residents will be achieved for the rural poor, and the proportion of reimbursement for hospitalization expenses within the scope of the rural poor policy will increase by 5 percentage points. Organize and mobilize more than 800,000 workers across the country to accurately investigate and verify 93 key diseases with high incidence and high expenses, which seriously affect production and living capacity, and establish health poverty alleviation work accounts and databases. Organize the classified treatment of rural poor people suffering from serious diseases and chronic diseases. As of May 2017, more than 2.6 million poor patients have been classified and treated nationwide. We will implement an accurate tilt payment policy for serious illness insurance, and give priority to the rural poor in terms of deductible, reimbursement ratio and capping line. We will promote the "one-stop" instant settlement of rural poor people who are hospitalized in the county before treatment. Arrange 889 tertiary hospitals across the country to undertake counterpart assistance tasks, and achieve full coverage of assistance to 1149 county-level hospitals in all poverty-stricken counties.
Six, the health level of specific groups has improved significantly.
China attaches great importance to protecting the health rights of specific groups, such as women, children, the elderly and the disabled, constantly improves health and health planning, provides diversified and targeted health services, and meets the special needs of all groups equally without discrimination.
The maternal and child health care service system has been continuously improved. Establish a three-level maternal and child health service network throughout urban and rural areas. In 2016, the state invested 2.9 billion yuan to support the construction of 247 municipal and county-level maternal and child health care institutions. By the end of 2016, there were 3,063 maternal and child health care institutions, 757 maternity hospitals, 117 children’s hospitals and 370,000 practicing (assistant) doctors in obstetrics and gynecology and pediatrics. In 34,000 community health service centers (stations), 37,000 township hospitals and 640,000 village clinics, there are full-time and part-time maternal and child health care workers.
The level of maternal health care services for women has been effectively improved. Since 2009, the country has expanded the coverage of cervical cancer and breast cancer screening programs for rural women year by year, and the number of beneficiaries has been increasing. From 2009 to 2016, the state conducted free cervical cancer screening for more than 60 million rural women aged 35 to 64 in 1,299 project counties, and invested 22.6 billion yuan to subsidize more than 74 million rural pregnant women. The hospital delivery rate of rural pregnant women increased from 92.3% in 2008 to 99.6% in 2016, and the maternal mortality rate and infant mortality rate in rural areas dropped significantly. The state has arranged subsidy funds to support the free pre-pregnancy eugenics health check-up project, the rural pregnant women’s hospital delivery subsidy project, the folic acid supplement project to prevent neural tube defects, and the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of AIDS, syphilis and hepatitis B. The objectives of the China Women’s Development Program (2011-2020) have been continuously realized.
The health level of children has improved significantly. In 2013, the exclusive breastfeeding rate of infants aged 0-6 months nationwide rose to 58.5%, and the breastfeeding rate continued to increase. In 2016, the infant mortality rate and the mortality rate of children under 5 years old were 7.5&permil respectively; And 10.2‰ All of them have achieved the United Nations sustainable development goals and the goals of the China Children’s Development Program (2011-2020) ahead of schedule, and the gap with developed countries has further narrowed. In 2016, the rates of underweight, growth retardation and anemia among children under five years old decreased to 1.49%, 1.15% and 4.79% respectively, and all of them achieved the goals of the China Children’s Development Program (2011-2020) ahead of schedule. By the end of 2016, 30 national demonstration bases for early childhood development had been established. We will carry out a nutrition improvement project for children in poverty-stricken areas, and provide a packet of supplementary food and nutrition supplements rich in protein, vitamins and minerals for children aged 6-24 months in contiguous areas with special difficulties. The results of the fifth survey of children’s physical development in China in 2016 show that in the last 40 years, the physical development level of children under 7 years old in China has increased rapidly, exceeding the standards for children’s growth and development promulgated by the World Health Organization.
The achievements in the prevention and treatment of childhood diseases have been consolidated. In 2016, the mother-to-child transmission rate of AIDS dropped to 5.7%, and the incidence of neonatal tetanus remained at 1‰ Below. The vaccination rate of children’s immunization program has remained above 99%, and it has remained polio-free, and the reported incidence of tuberculosis in children has remained at a low level. In 2016, the screening rate of hereditary metabolic diseases (phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism) reached 96%, and the implementation scope of neonatal disease screening project in poverty-stricken areas has covered 354 counties (cities, districts) in 21 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). We will implement major public health service projects such as free pre-pregnancy eugenics health examination, neonatal disease screening in poverty-stricken areas, and thalassemia prevention and control pilot projects.
The health service system for the elderly is improving day by day. By the end of 2015, there were 453 rehabilitation hospitals, 168 nursing homes and 65 nursing stations in China, increasing by 69.0%, 242.9% and 16.1% respectively compared with 2010. The number of health workers in rehabilitation hospitals, nursing homes and nursing stations in China was 36,441, 11,180 and 316 respectively, increasing by 96.5%, 286.7% and 69.9% respectively compared with 2010. In 2015, the state provided 118 million physical examinations for the elderly aged 65 and over, and the health management rate reached 82%. The mental health of the elderly has been fully concerned, and the state and society have publicized mental health knowledge and provided psychological counseling to the elderly through various forms to enrich their spiritual and cultural life.
The service mode of combining medical care with nursing care was further promoted. In 2016, 90 cities (districts) were selected and identified as national-level pilot units for the combination of medical care and nursing. There are 5,814 medical and nursing institutions in China, with a total of 1,213,800 beds. Among them, 3,623 medical institutions were set up in the old-age care institutions, 1,687 were set up in the medical institutions, and 504 were set up at the same time, and 2,224 were included in the designated scope of medical insurance. Actively carry out special actions to build the service quality of nursing homes, improve the quality control system, and significantly improve the service quality of medical and nursing institutions.
Disability prevention and rehabilitation services for the disabled have been continuously strengthened. In 2016 and 2017, the State promulgated the National Action Plan for Disability Prevention (2016-2020) and the Regulations on Disability Prevention and Rehabilitation of Persons with Disabilities, respectively, and the work of disability prevention and rehabilitation of persons with disabilities was brought into the development track of the rule of law. From 2012 to 2016, a total of 15.26 million disabled people in China received basic rehabilitation services. By the end of 2016, there were 7,858 rehabilitation institutions for the disabled in China, with 223,000 employees on the job, and 947 municipal districts and counties (cities) in 2015 carried out community rehabilitation work, with 454,000 community rehabilitation coordinators. Since 2017, the state has designated August 25th as "Disability Prevention Day".
The coverage of rehabilitation sports for the disabled has gradually expanded. Promote basic public services for disabled sports in the 13th Five-Year Plan. We implemented the regional guidance policy of "from west to east", "from north to south" and "weak first and then developed", funded 8,000 rehabilitation sports projects in six western provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), instigated 88,884 national services, subsidized 50 new community fitness demonstration sites, and instigated 1,842 new ones nationwide. The proportion of disabled people who regularly participate in physical fitness activities in China has increased to 9.6%.
Disabled orphans receive special care. Since 2015, the state has included sick and disabled children with surgical indications among urban and rural minimum living allowances and destitute support objects, as well as orphans and disabled children scattered in society in the scope of funding for the Tomorrow Plan, implemented medical rehabilitation with reference to the treatment policies and practices of orphans and disabled children in welfare institutions, and integrated tens of thousands of children recovered after the Tomorrow Plan into society. All new children with surgical indications in welfare institutions can get surgical treatment at the best treatment opportunity. By the end of 2016, the state had invested 860 million yuan to carry out surgical correction and rehabilitation training for more than 90,000 disabled orphans.
7. Actively participate in global health governance and international medical assistance.
China is an advocate, promoter and practitioner of international cooperation in the field of health care. It has always been committed to realizing the Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development, fully implementing the UN’s 2030 sustainable development agenda, especially the sustainable development goals in the health field, actively carrying out foreign medical assistance and global emergency response, earnestly fulfilling international conventions in the health field, and courageously assuming international humanitarian responsibilities.
Participate in the construction of international rules system of medical and health care. China signed and ratified the Constitution of the World Health Organization earlier, joined the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs and the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, participated in the formulation of a series of international treaties and declarations such as the Almaty Declaration, and responded to the World Declaration on the Survival, Protection and Development of Children. In 2016, at the 69th World Health Assembly, China proposed and promoted the adoption of the resolution "Promoting innovation and obtaining safe, effective and affordable quality medicines for children", which received positive responses from all parties.
In-depth cooperation with the World Health Organization. In 2016, the China-World Health Organization Country Cooperation Strategy (2016-2020) was signed and released in Beijing, which defined cooperation in the fields of health policy, planning, technology and human resources. In 2017, we signed the Memorandum of Understanding on the Belt and Road Health Cooperation and the Implementation Plan on the Belt and Road Health Cooperation, and worked together to cooperate with countries along the Belt and Road in the fields of health emergency, infectious disease prevention and traditional medicine.
International medical and health exchanges and cooperation are constantly expanding. China conducts experience sharing and strategic dialogue with other countries in the field of health, and holds international seminars in various fields of medical and health services every year. In December 2015, the China-Africa public health cooperation plan was announced at the Johannesburg Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, including important measures such as participating in the construction of the African CDC. In October 2016, it established cooperative relations with counterpart hospitals in 15 Asian and African countries, including Ethiopia. In April 2017, it signed a medical and health cooperation agreement with African countries such as Malawi. Since 2005, China has trained thousands of officials and technical service personnel from developing countries, and promoted China non-governmental organizations to carry out education and training programs on adolescent reproductive health and AIDS prevention in Zimbabwe, Kenya and other countries and the Mekong region.
Outstanding achievements have been made in foreign medical and health assistance. Since 1963, China has sent foreign aid medical teams to 69 developing countries, with a total of 25,000 medical team members and 280 million patients treated. In September 2015, China announced at a series of UN summits that it would provide 100 hospitals and clinics and implement 100 "maternal and child health projects" and other major health assistance initiatives for developing countries in the next five years. By June 2017, China had more than 1,300 medical team members and public health experts working in 51 countries around the world, trained more than 20,000 international medical and health management and technical personnel in China, built more than 150 landmark facilities such as general hospitals, specialist centers and drug warehouses, provided many batches of medical materials such as ambulances, diagnostic instruments and cold chains of vaccines, and donated antimalarial drugs to Africa, saving 40 million lives. Since 2008, China has set up 30 malaria control centers for African countries, providing artemisinin antimalarial drugs worth 190 million yuan.
Global emergency response has been effectively carried out. China meets the compliance standards of the International Health Regulations. Actively lead international emergency rescue operations, and successively joined in responding to yellow fever and Zika virus in Angola and Guyana. In 2014, Ebola hemorrhagic fever broke out in West Africa, and China provided cash and materials to countries and international organizations in the affected areas for four consecutive rounds, with a total value of US$ 120 million. More than 1,200 medical staff and public health experts were sent to epidemic areas and neighboring countries, and nearly 9,000 samples were tested, more than 900 cases were observed and treated, and 13,000 local medical care and community prevention and control backbones were trained. In 2015, an earthquake of magnitude 8.1 occurred in Nepal. China successively coordinated and arranged four China government medical and epidemic prevention teams with a total of 193 people to go to the disaster-stricken areas in Nepal to carry out rescue, treating more than 2,600 wounded people and training more than 1,000 health and epidemic prevention technical backbones.
The international recognition of traditional Chinese medicine has been continuously improved. Chinese medicine has spread to 183 countries and regions around the world, and has become an important part of China’s cooperation with ASEAN, Europe, Africa and other regions and WHO. "Acupuncture in Traditional Chinese Medicine" is listed in UNESCO’s representative list of intangible cultural heritage of mankind, and Huangdi Neijing and Compendium of Materia Medica are selected in the world memory list. According to the statistics of the World Health Organization, 103 Member States have approved the use of acupuncture, of which 29 have established laws and regulations on traditional medicine, and 18 have included acupuncture in the medical insurance system.
Concluding remarks
The governments of the Communist Party of China (CPC) and China earnestly respect and protect people’s right to health, regard safeguarding people’s health as the basic task of governing the country, and have implemented a series of major measures that benefit the present and benefit the long term. China’s health cause has made great achievements that attract worldwide attention and made important contributions to the sustainable development of mankind.
"Life is between heaven and earth, and there are dangers in the long road". China is soberly aware that ensuring people’s health is a systematic project, which needs long-term sustained efforts. At present, due to industrialization, urbanization and aging population, China still faces a complicated situation in which multiple disease threats coexist and multiple health influencing factors are intertwined. At the same time, with the improvement of living standards and the enhancement of health concept, the people’s demand for health products and services continues to grow, and it presents the characteristics of multi-level, diversification and personalization. China is facing the health problems faced by both developed countries and developing countries.
In order to better protect the people’s right to health, China is stepping up the construction of a healthy China, and has formulated and implemented a series of planning outlines such as "Healthy China 2030", "National Fitness Program (2016-2020)", "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan" and "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan for Deepening the Reform of Medical and Health System", and put forward the goal of "three steps" By 2030, the institutional system for promoting national health will be more perfect, and the main health indicators will enter the ranks of high-income countries; By 2050, we will build a healthy country that is compatible with the socialist modern country. With a high sense of responsibility and urgency, governments at all levels in China will continue to ensure people’s health in an all-round and full-cycle way, and strive to promote the all-round development of health and health undertakings.
Health is the eternal pursuit of mankind, and health promotion is the common responsibility of the international community. The United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development identified health as an important sustainable development goal, and the global health system is in an important period of development. China will, as always, actively participate in international activities in health-related fields, deeply participate in global health governance, and vigorously implement the sustainable development goals in the health field. By cooperating with the construction of the "Belt and Road", we will enhance cooperation with countries along the route in the field of health and health, and strengthen mutual learning and learning with countries around the world. In the great process of "building a community of human destiny together", China is willing to join hands with the people of the world and make unremitting efforts to build a better and healthier world.
