The cancer mortality rate of men in China is higher than that of women, and these cancers are more likely to be obtained in developed areas.
Recently, the authoritative journal of oncology in China, Chinese Journal of Oncology, published the Analysis of the Epidemic Situation of Malignant Tumors in China. The report published the incidence and death of cancer in China, and for the first time provided the epidemic situation of major cancer spectrum in various provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government).
Malignant tumor has always been a major cause of death among domestic residents. The national death cause monitoring report shows that malignant tumor ranks first in the cause of death, accounting for 24.09% of all deaths, which is higher than the global average of 17.83%.
The incidence and mortality of lung cancer are the highest.
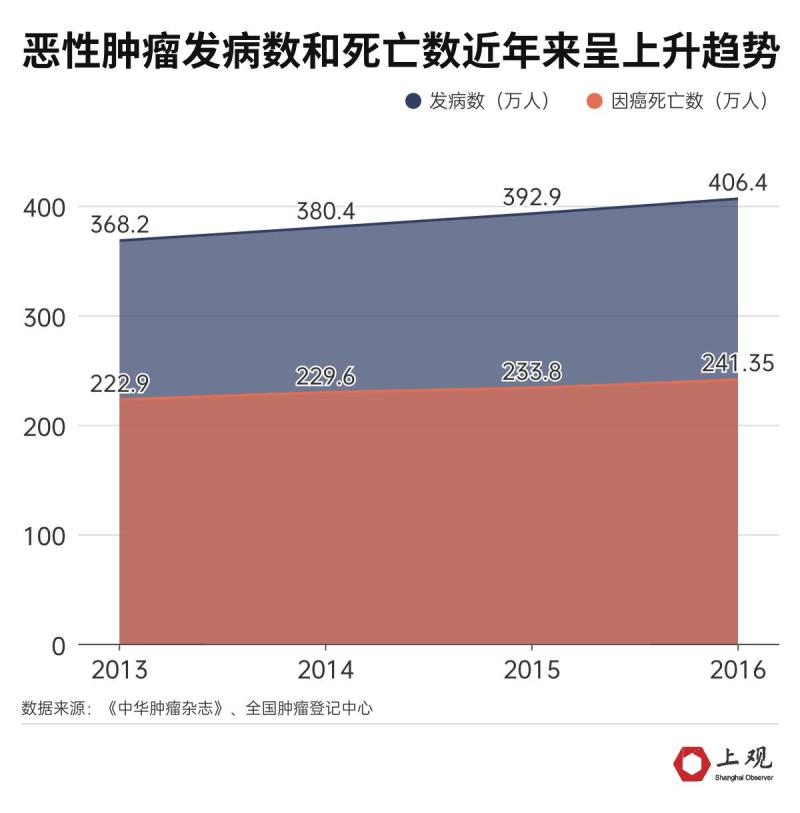
In recent years, the number of people suffering from cancer and the number of people who died of cancer in China have been rising. According to the latest data, there are about 4,064,000 new cases of malignant tumors in China, including 2,234,300 males and 1,829,600 females, with a crude incidence rate of 2,939.1/100,000.
The data show that the most common malignant tumor in China is lung cancer, with the incidence of 828,100 cases and the crude incidence rate of 58.89/100,000, accounting for more than 20% of all malignant tumors. This means that in China,One out of every five patients with malignant tumor is a lung cancer patient.. Globally, lung cancer accounts for 11.6% of all malignant tumors, which shows that lung cancer is relatively high in China.
In addition, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer and breast cancer are also malignant tumors with high incidence in various places, ranking among the top five malignant tumors with the highest incidence in China, just like lung cancer.
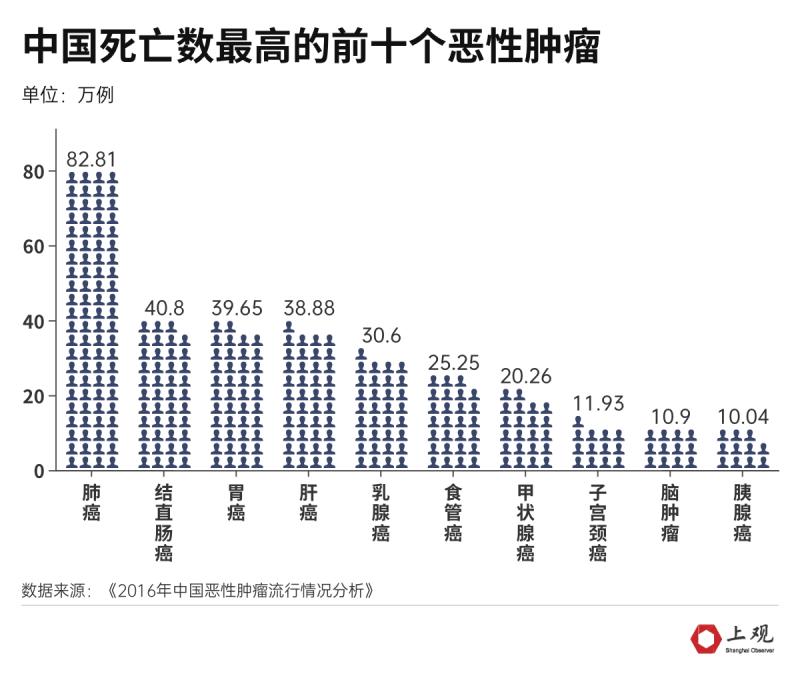
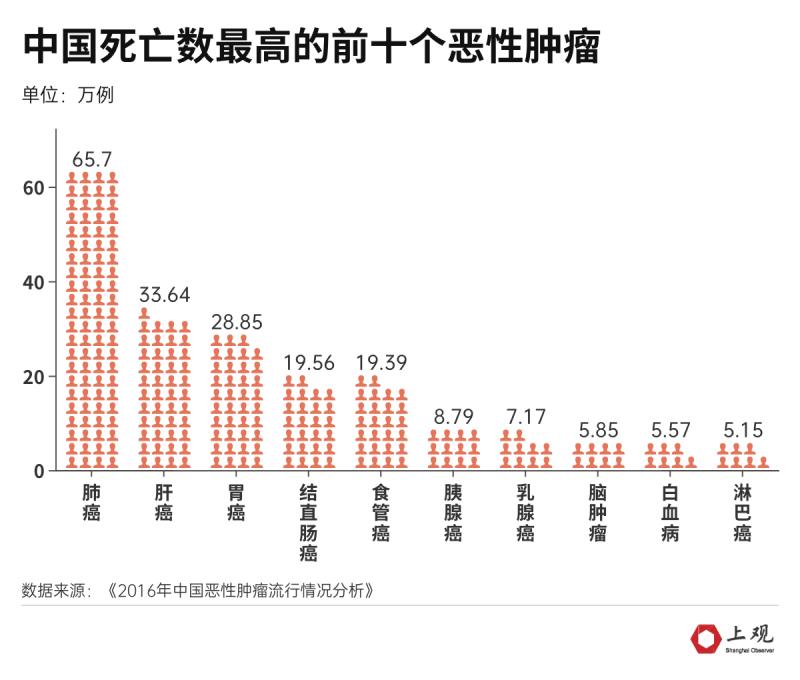
Lung cancer is also the first malignant tumor with the highest mortality rate in China, followed by liver cancer and gastric cancer. Among the top ten malignant tumors with the highest number of deaths, high-incidence malignant tumors such as colorectal cancer and esophageal cancer also entered the list. In addition, the incidence of leukemia and lymphoma was relatively low, but the number of deaths was high, which also entered the top ten.
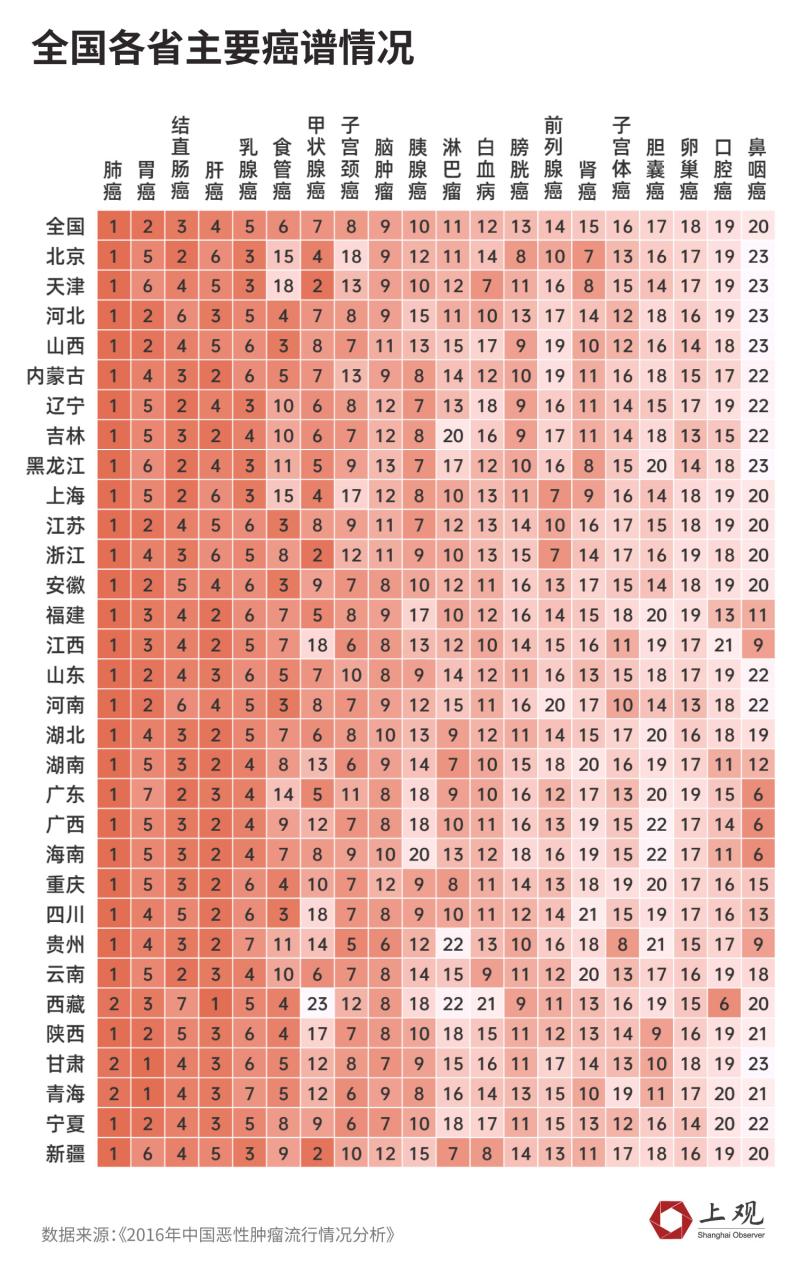
The incidence of lung cancer is the highest
In all provinces of China, lung cancer is the most common cancer except Tibet, Gansu and Qinghai. The highest incidence in Gansu and Qinghai in the northwest is gastric cancer, and the highest incidence in Tibet is liver cancer.
Colorectal cancer, as a "rich disease" with higher incidence in areas with high human development index (HDI), is the second most common category in Beishangguang.
Esophageal cancer, which is considered to be related to eating pickled food, is high in Sichuan, Jiangsu, Anhui and Henan, ranking third.
In addition to the top five malignant tumors, there are more differences in the incidence of different malignant tumors between regions.
Nasopharyngeal cancer ranks 20th in the incidence order of malignant tumors in China, but it ranks in the top 10 in Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Guizhou and Jiangxi in the south, while it is less common in the north. For example, in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi, Heilongjiang and Gansu, the number of patients with nasopharyngeal cancer ranks 23rd.
Thyroid cancer is the second largest cancer after lung cancer in Tianjin, Zhejiang and Xinjiang, and the incidence of thyroid cancer ranks seventh nationwide.
Overall,Colorectal cancer, prostate cancer and breast cancer are more common in developed areas.
Shanghai’s cancer survival rate has improved.
Cancer is the second cause of death among Shanghai residents.
According to the latest data released by the Shanghai Municipal Health and Health Commission, the three most common cancers in Shanghai areLung cancer, colorectal cancer and thyroid cancer.
According to the latest data released this year by Shanghai Health and Health Commission, with the improvement of medical conditions, the promotion of early screening, health education and health promotion of cancer prevention and treatment, the five-year survival rate of cancer patients in Shanghai has reached 56%, which has been rising continuously for more than ten years.
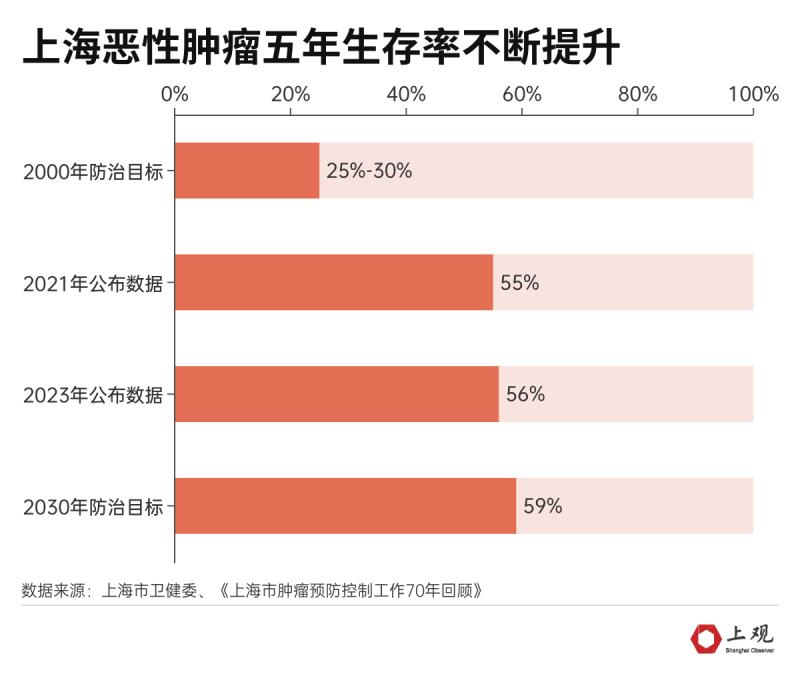
In addition, the early diagnosis rate of common malignant tumors in Shanghai has increased to 42%, which is 3 percentage points higher than the data published in 2021, which has won prime time for the treatment of more patients.
As far as the incidence and mortality of cancer in Shanghai are concerned, the incidence rate has increased from 5.46/100,000 two years ago to 6.23/100,000, and the mortality rate has increased from 2.56/100,000 to 2.61/100,000. Experts believe that this is mainly caused by the aging population structure in Shanghai. After removing the aging factor, the standardized cancer mortality rate of Shanghai residents is lower than the national average, which is 42% lower than that of more than 40 years ago.
It is worth noting that since 2013, the community colorectal cancer screening in Shanghai has achieved remarkable results. This year, it will continue to implement the "colorectal cancer screening for community residents" and provide free colorectal cancer screening services to 400,000 residents.
The cancer mortality rate of men is higher than that of women.
There are obvious differences in cancer burden between urban and rural areas and between men and women.
On the whole, the cancer burden in cities is heavier than that in rural areas.
The incidence of urban malignant tumors is 2,495,900, accounting for 61.41% of the total incidence. You know, the proportion of permanent residents in cities and towns to the total population was 57.35%. The number of cases in rural areas is 1,568,100, accounting for 38.59%.
In terms of incidence, the incidence of malignant tumors in urban areas is 1.9638/100,000, which is 7.8% higher than that in rural areas (182.21/100,000).
From the cancer spectrum of high incidence, lung cancer is the most common cancer in both urban and rural areas, and the second highest incidence in urban areas is colorectal cancer, while in rural areas it is gastric cancer.
cityThe top five high-incidence malignant tumors in the region are as followsLung cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer and female breast cancer.The top five high-incidence malignant tumors in rural areas are lung cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer.
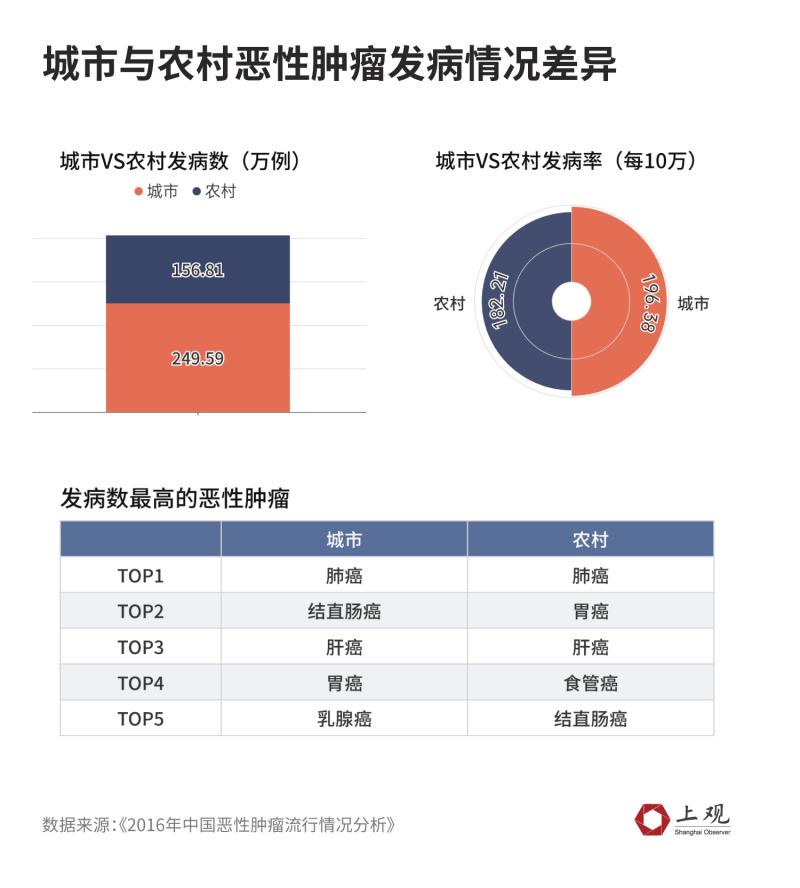
However,The mortality rate of malignant tumors in urban areas is lower than that in rural areas.The standardized mortality rate of malignant tumors in urban areas is 104.44/100,000, and that in rural areas is 108.01/100,000.
In terms of gender, the incidence rate of women in the age group of 15~49 is higher than that of men, and that of men over 50 is higher than that of women; However, the cancer mortality rate of men is significantly higher than that of women after 35 years old, and the difference increases with age.
The most common cancers in men are lung cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer, while those in women are breast cancer, lung cancer and colorectal cancer.
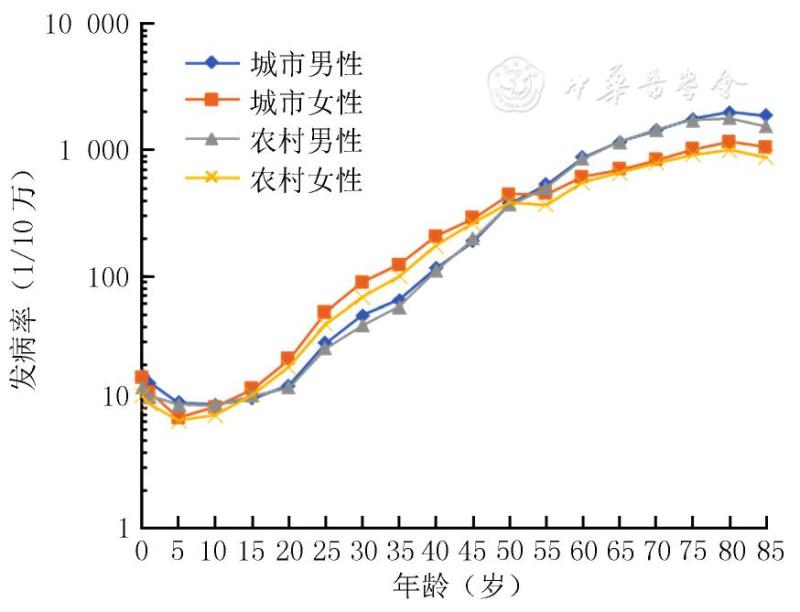
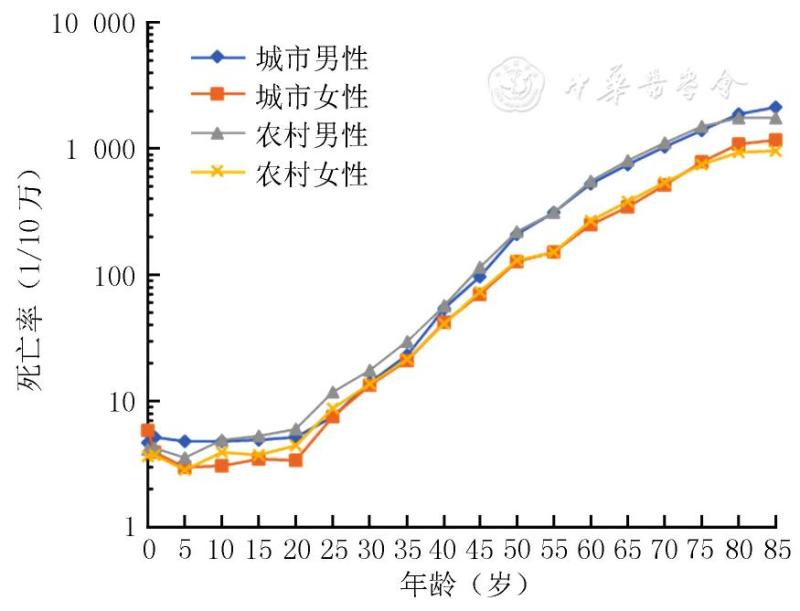
In addition, in the incidence spectrum of men, prostate cancer and bladder cancer have an obvious upward trend in recent years, ranking sixth and seventh respectively, which should be paid special attention to in the future tumor prevention and control.